A computer-generated world that a user may explore and interact with is referred to as a virtual reality (VR) environment. A simulated 3D environment called virtual reality allows users to explore and interact with a virtual environment in a fashion that simulates reality as it is experienced by the users’ senses. Although the environment is built using computer hardware and software, users may also need to put on accessories like helmets or goggles in order to interact with it. Users are better able to suspend disbelief and treat a VR experience as real, even if it is fanciful, the more fully they can immerse themselves in it and block out their physical surroundings. The brain is essentially manipulated into believing that what a user is experiencing in the virtual world is real by immersing them in it.
Types of virtual reality
The VR industry still has a long way to go before achieving its goal of creating a fully immersive setting that allows users to experience a variety of feelings in a manner that is close to reality. However, the technology has advanced significantly in terms of delivering a genuine sensory experience and holds potential for commercial application in a number of areas. Depending on their function and the technology employed, VR systems can vary greatly from one to the next, but they typically fall into one of the following three categories:
Non-immersive Virtual Reality. Typically, a 3D simulated environment that can be accessed through a computer screen is what is meant by this kind of VR. Depending on the software, the surroundings might also produce sound. Using a keyboard, mouse, or other device, the user can influence the virtual world to some extent, but the environment does not communicate with the user directly. Non-immersive VR is exemplified by video games and websites that let users customize the look of a room.
Semi-immersive Virtual Reality. Through a computer screen, a pair of glasses, or a headset, this kind of VR provides a limited virtual experience. It does not involve physical movement like full immersion does and instead concentrates on the visual 3D part of virtual reality. The flight simulator, which is used by airlines and military to train their pilots, is a typical example of semi-immersive VR.
Fully immersive Virtual Reality. The user is entirely submerged in the virtual 3D environment thanks to this type of VR, which offers the highest quality of virtual reality. It includes hearing, seeing, and occasionally touching. Even some attempts with the addition of smell have been conducted. Users are able to completely interact with their surroundings when they are wearing specialized gear like helmets, goggles, or gloves. To give consumers the feeling of moving across the 3D world, the environment may also include items like treadmills or stationary bicycles. Although fully immersive VR technology is still in its infancy, it has already had a significant impact on the gaming and, to a lesser extent, the healthcare industries, and it is sparking a lot of interest across a variety of other industries.
Automotive sector
Before ordering pricey prototypes, engineers and designers can readily experiment with the design and construction of a vehicle using virtual reality. Before any money is spent on physically building the pieces, companies have been using VR for years to undertake early design and engineering assessments to examine the visual design and object obscuration of the vehicle. VR is saving the automotive industry millions by reducing the number of prototypes built per vehicle line.
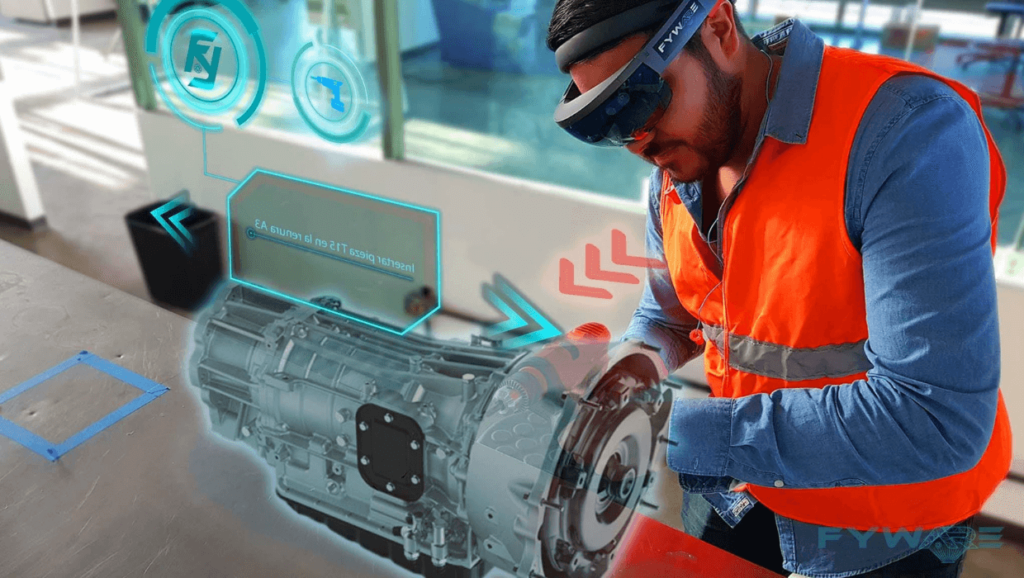

Healthcare
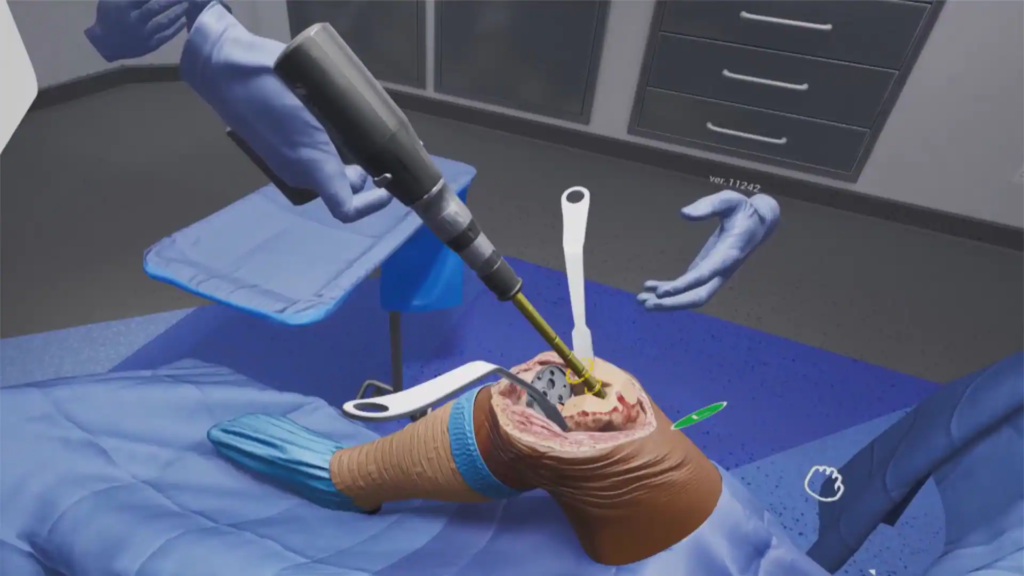
VR is having a big impact on the medical industry. Anonyms medical company authorized EaseVRx for prescription usage in November 2021 for the management of adult pain reduction. The approach reduces chronic pain by utilizing cognitive behavioral therapy as well as other behavioral concepts including interoceptive awareness, deep relaxation, and attention-shifting, among others. Even burn injuries have been treated with VR to reduce discomfort. Healthcare personnel can use virtual reality (VR) to better prepare themselves for being in the operating room, whether as an orthopedic surgeon doing surgery or a younger doctor outlining diagnosis and treatment plans. Companies are giving surgeons the ability to perform surgery on virtual patients and interface with medical devices in virtual reality, which helps them become more proficient at implanting new devices and comfortable with them. Virtual Reality (VR) can also be used to treat mental health conditions, with Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy (VRET) being especially useful for treating PTSD and anxiety. There are numerous additional ways that engaging in VR can be therapeutic.
Retail
With “the virtual world,” our online shopping habits are about to undergo a significant transformation. We will be able to try on clothing virtually to see how it might appear on us thanks to body-scanning technologies and virtual reality retail experiences. Consumers will know before they order whether the item suits their shape and size, which lowers the environmental cost of manufacture and delivering quick fashion. This saves customers’ time while also being more sustainable.
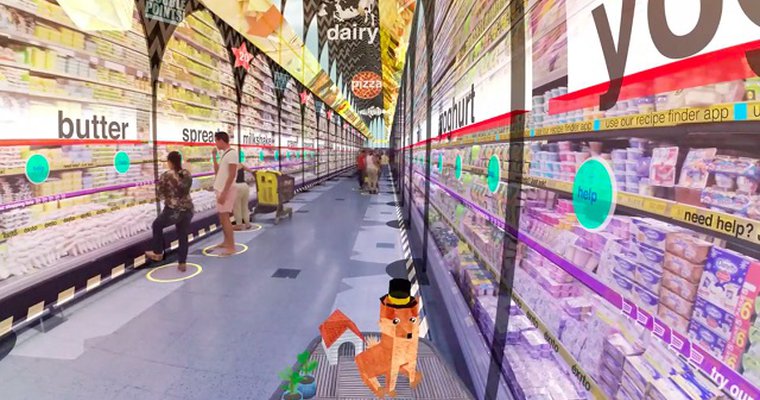

Tourism
Virtual reality is one of the most important advancements in information and communication technology (ICT) that is now anticipated to have a substantial impact on the tourism sector (VR). The evolution of VR is made possible by many recent innovations, including VR platforms, devices, and content production tools. Because of this, VR technologies now have limitless potential for enabling widespread virtual travel to actual tourist places. Additionally, the management and marketing functions of these technologies in the tourism and hospitality sectors have been described in literature as being able to demonstrate their intricate capacities to simulate real-life situations and contexts, occasionally being promoted as a replacement for actual travel, making it a very potent tool for catering to the needs of tourists.

Real estate
There is no need to schedule appointments with estate agents or give up your weekend if you’d rather stay closer to home. You can browse houses from the convenience of your current home. Businesses are paving the way for individuals to view homes online and get a sense of the space, saving time spent touring homes that might be smaller, more cluttered, or otherwise not what you imagined. By doing this, you can concentrate your time on seeing only the properties in person that you’re most likely to adore.

Architecture
Architecture is gradually altering as a result of virtual reality (VR). With VR, it’s possible to visualize both the appearance and feel of a building or location. For instance, if someone wanted to extend their home, they could view the room and how it would appear before it was really built, and then make adjustments in real time. By doing this, the client and the architect are able to complete the project more quickly and more affordably while also feeling more satisfied.
Interior design
In VR, your house’s structure isn’t the only thing receiving a facelift. Now, you may recreate the interior design using immersive experiences. Businesses are taking advantage of this by offering users 3D representations of the inside of their house or place of business, including details on lighting, ventilation, color schemes, and the products themselves. Platforms like this have the potential to increase direct sales for furniture businesses like Ikea in addition to assisting designers and homeowners in visualizing the look and feel of a house.
Learning and development
People can learn through experience in a risk-free environment using VR; it is reliable, cost-effective, and scalable. Virtual reality not only addresses the most important concerns in employment today, but it also has a number of advantages that any company or business will be delighted to have. Virtual reality replicates real-world situations, therefore it also eliminates risks that might otherwise exist in reality. A safer way to learn will be made possible by the use of VR for employee training, especially for individuals who undertake tasks that include physical risks. Virtual reality will be very helpful in the training of security forces as well as jobs like engineering and shipping. It will also help with power grid maintenance. Virtual reality equipment runs on programs that are designed based on a company’s demands. Great customization is made possible by this, which also lowers prices. Companies won’t have to construct brand-new training facilities in order to teach employees new skills that may be required in the future. Additionally, using virtual reality lowers training expenses for programs that need resources in many areas, such as manufacturing and the restaurant and catering sectors. Virtual reality can aid in the development of empathy even though it cannot instigate it. Empathy is crucial for leaders and a crucial component of teamwork. Additionally, it has been found that empathic workers perform better in customer service roles, which are crucial in service-based industries.

